The Power of Autophagy: Definition, Health Benefits, Regulation and Inhibitors, and Biological Functions
If you’re interested in health and wellness, you might have heard about autophagy. This natural process is critical for keeping our cells healthy and functioning optimally. In this article, we’ll explore what it is, how it works, and the many health benefits it offers. We’ll also delve into the regulation and inhibitors of it, as well as its biological functions. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- What is Autophagy?
- The Autophagy Process
- Health Benefits of Autophagy
- Regulation and Inhibitors of Autophagy
- Biological Functions of Autophagy
What is Autophagy?
It is a natural process that occurs within our cells. It’s a Greek word that means “self-eating,” and that’s exactly what it is. It is the process by which our cells break down and recycle old, damaged, or unnecessary components, such as proteins, organelles, and even entire cells. This process allows our cells to maintain their health and function optimally.
The Autophagy Process
The autophagy process is a highly regulated and intricate process that involves several steps:
Initiation
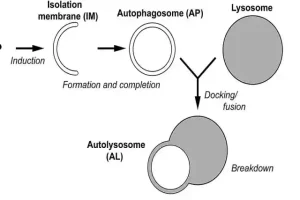
The initiation step of autophagy is a critical first step in the process. It all starts with the formation of a double-membrane structure called an autophagosome. This structure essentially engulfs the old or damaged cellular components that need to be broken down and recycled, marking them for removal from the cell.
The formation of the autophagosome involves a complex interplay between various proteins and signaling pathways within the cell. Essentially, the cell needs to recognize the need for autophagy and activate the machinery required to form the autophagosome.
Once formed, the autophagosome can then move on to the next step of the autophagy process – maturation. It’s amazing to think about how something as small as a membrane structure can play such a crucial role in maintaining the health of our cells and ultimately our overall well-being.
Maturation
After the autophagosome is formed, it moves towards the lysosome, which contains digestive enzymes. Once the autophagosome fuses with the lysosome, it forms an autolysosome.
Inside the autolysosome, the lysosome breaks down the contents of the autophagosome into smaller components, including amino acids, lipids, and nucleotides. These molecules can then be used by the cell to produce energy or build new cellular components.
This process of maturation and breakdown is essential for the proper functioning of autophagy. Without it, the cell would not be able to recycle its components efficiently and may accumulate damaged or unnecessary components, leading to disease and aging.
It’s worth noting that the process of autophagy is not always perfect, and sometimes damaged or unnecessary components may escape the recycling process. However, the cell has other mechanisms in place to deal with these components, including the ubiquitin-proteasome system.
Termination
After the autophagosome fuses with the lysosome to form an autolysosome, the lysosome starts breaking down the contents of the autophagosome. This is the stage where damaged cellular components are degraded and their breakdown products are released back into the cytoplasm. These breakdown products are amino acids and other molecules that can be used by the cell to create new proteins or other cellular components.
This process of recycling cellular components is vital for maintaining cellular health and preventing the buildup of harmful waste products. Once the autophagy process is complete, the autolysosome breaks down and releases the products of autophagy back into the cytoplasm.
It’s important to note that it is a continuous process that occurs throughout our lives. It plays a critical role in maintaining the health of our cells and preventing various diseases, making it an essential biological process to understand and study.
It can be categorized into three different types, including macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy. Each type of autophagy involves a different mechanism for the breakdown and recycling of cellular components.
Health Benefits of Autophagy
It plays a critical role in maintaining our overall health and preventing various diseases. Here are some of the health benefits associated with autophagy:
Autophagy and Cancer
It’s relationship with cancer is complex and multifaceted. On one hand, it can be beneficial in preventing the development of cancer. By eliminating damaged or mutated cells that could potentially become cancerous, it acts as a defense mechanism for the body.
However, it can also help cancer cells survive and thrive under stressful conditions. In some cases, cancer cells can use it to recycle and generate nutrients, allowing them to resist treatments like chemotherapy and radiation.
As a result, researchers are exploring the potential of targeting it as a strategy for cancer therapy. By inhibiting autophagy, it may be possible to weaken cancer cells and enhance the effectiveness of existing treatments. However, it’s important to note that it plays a complex role in cancer, and further research is needed to fully understand its role in the development and progression of the disease.
Autophagy and Aging
As we age, the efficiency of the autophagy process decreases, which can lead to the accumulation of damaged cellular components. This buildup can contribute to the development of age-related diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and cardiovascular disease.
Promoting it through lifestyle changes such as fasting and exercise can help slow down the aging process and reduce the risk of age-related diseases. By enhancing the body’s natural waste removal system, it can eliminate harmful cellular components and promote the production of new, healthy cells.
Recent studies have also shown that it may play a role in extending lifespan. By promoting autophagy, we may be able to slow down the aging process and live longer, healthier lives.
So, if you’re looking to promote longevity and prevent age-related diseases, why not give autophagy-promoting lifestyle changes a try? Simple habits like intermittent fasting and regular exercise may hold the key to a healthier, happier, and longer life.
Autophagy and Fasting
Fasting is not just about restricting calorie intake – it can actually promote autophagy, the process by which our cells break down and recycle old, damaged, or unnecessary components.
When we fast, our cells are deprived of nutrients, which triggers the activation of the autophagy process. This can lead to the breakdown of old and damaged cellular components, allowing for the recycling of nutrients that can be used by the body.
Promoting autophagy through fasting has been shown to provide various health benefits, such as reducing the risk of chronic diseases, improving metabolic function, and promoting longevity. However, it’s important to note that fasting should be done safely and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially for those with certain medical conditions.
Autophagy and Exercise
Regular exercise not only has physical health benefits but also promotes autophagy, which is the process by which our cells recycle old, damaged, or unnecessary components.
During exercise, our cells undergo stress, which can activate the autophagy process. This means that the cellular components that are no longer needed or damaged are targeted for recycling. This breakdown of cellular components can help prevent various diseases and improve overall health.
Additionally, studies have shown that regular exercise can increase autophagy levels in our cells, promoting the removal of harmful proteins that can contribute to the development of diseases. So, by incorporating exercise into our daily routine, we can promote autophagy and improve our overall health and well-being.
Autophagy and Neurodegeneration
Autophagy plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of our nervous system. When autophagy doesn’t function properly, it has been linked to various neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. These diseases are characterized by the accumulation of damaged proteins and cellular components in the brain, which can lead to cognitive decline and impaired motor function.
Research suggests that promoting autophagy may reduce the risk of developing these diseases and improve overall brain health. In fact, some studies have found that inducing autophagy can improve the clearance of toxic proteins in the brain, potentially slowing down the progression of these diseases.
It’s important to note that while there is still much to learn about the relationship between autophagy and neurodegeneration, promoting autophagy may be a promising approach for preventing or treating these devastating diseases.
Autophagy and Inflammation
Autophagy plays an important role in regulating inflammation in our bodies. When our cells are damaged, they can release proteins that trigger inflammation, leading to chronic inflammation and various diseases. However, autophagy can prevent this from happening by breaking down these harmful proteins and preventing their accumulation.
By reducing chronic inflammation, autophagy may help reduce the risk of several diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. In fact, studies have shown that promoting autophagy can improve various markers of inflammation and may even improve overall immune function.
So, if you’re looking for ways to improve your immune system and reduce your risk of chronic diseases, promoting autophagy may be a great place to start. Simple lifestyle changes like intermittent fasting and regular exercise have been shown to stimulate autophagy and provide various health benefits, including reduced inflammation.
Autophagy and Mitochondria
Our mitochondria, the energy-producing organelles in our cells, are crucial to our overall health and well-being. Dysfunctional mitochondria can lead to the production of harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage cellular components and contribute to the development of various diseases.
Luckily, autophagy is here to help. Autophagy plays a vital role in maintaining the health of our mitochondria by eliminating damaged components and preventing the production of harmful ROS. This process can provide various health benefits, including reducing the risk of age-related diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
By promoting autophagy, we can support the health of our mitochondria and prevent the accumulation of harmful ROS, promoting overall health and well-being. So, whether it’s through fasting or exercise, it’s important to incorporate autophagy-promoting habits into our daily lives to ensure the optimal health of our mitochondria and ourselves.
Regulation and Inhibitors of Autophagy
Autophagy is a tightly regulated process that can be influenced by various factors, including nutrient availability, stress, and hormonal signals. Several genes have been identified that play a critical role in regulating autophagy, including the mTOR pathway, which acts as a central regulator of autophagy.
Several drugs and compounds have also been found to either promote or inhibit autophagy. For example, rapamycin, a drug used to treat cancer and prevent organ rejection, has been found to promote autophagy. Conversely, chloroquine, an anti-malarial drug, has been found to inhibit autophagy.
Biological Functions of Autophagy
Autophagy plays a critical role in various biological functions, including:
Autophagy and the Immune System
One way autophagy supports the immune system is by helping immune cells develop and mature properly. Autophagy is involved in the degradation and recycling of cellular components that are no longer needed, which is essential for the proper maturation of immune cells.
In addition to its role in immune cell development, autophagy is also involved in the elimination of invading pathogens. When a pathogen enters our body, autophagy can engulf and break down the pathogen, preventing its replication and spread. Autophagy is particularly important for eliminating intracellular pathogens, which can hide inside cells and evade other immune defenses.
Overall, autophagy is crucial for maintaining a healthy and functional immune system, which is essential for fighting off infections and preventing diseases. By promoting autophagy, we may be able to boost our immune system and improve our overall health.
Autophagy and Apoptosis
Autophagy and apoptosis, which is the process of programmed cell death, are closely related. In fact, autophagy can play a critical role in regulating apoptosis and promoting cell survival.
When autophagy is dysfunctional, damaged cellular components can accumulate and trigger apoptosis. This can be detrimental to the health of our cells and can even contribute to the development of various diseases.
However, autophagy can help prevent the accumulation of these components and promote cell survival. By breaking down and recycling these components, autophagy can remove potential triggers for apoptosis and promote the health and longevity of our cells.
In some cases, autophagy can even trigger a process called “autophagic cell death,” which involves the selective destruction of certain cellular components to promote the death of cancerous or infected cells.
Overall, the relationship between autophagy and apoptosis is complex, with autophagy playing a critical role in promoting cell survival and preventing the accumulation of damaged cellular components that can trigger apoptosis. By understanding this relationship, we can work towards promoting healthy autophagy and preventing the development of various diseases.
Autophagy and Metabolism
Autophagy also plays a critical role in regulating cellular metabolism, which is the process by which our cells convert nutrients into energy. During times of nutrient deprivation, such as fasting or exercise, our cells may rely on autophagy to provide energy.
Through autophagy, cellular components are broken down and their nutrients are recycled, providing a source of energy for the cell. This process can be especially important in situations where nutrients are scarce, as it allows the cell to continue functioning and producing energy even in the absence of external nutrients.
Overall, the ability of autophagy to regulate cellular metabolism highlights its importance in maintaining the overall health and function of our cells. By recycling nutrients and providing energy during times of nutrient deprivation, autophagy can help promote cell survival and prevent various diseases.
Autophagy and Protein Degradation
In addition to breaking down and recycling cellular components, autophagy is also involved in the degradation of proteins. By targeting damaged or misfolded proteins for degradation, autophagy helps prevent the accumulation of harmful proteins that can contribute to the development of various diseases.
When proteins become damaged or misfolded, they can no longer perform their normal functions and may even become toxic to the cell. This is particularly true in conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, where the accumulation of toxic proteins can lead to neuronal damage and cognitive decline.
However, autophagy can help prevent the accumulation of these toxic proteins by targeting them for degradation. By breaking down these proteins, autophagy helps maintain cellular health and prevent the development of diseases associated with protein accumulation.
Therefore, promoting autophagy through lifestyle changes like fasting and exercise can have significant benefits for the prevention and management of protein-related diseases.
Autophagy and Cell Death
Autophagy not only helps recycle cellular components, but it also plays a crucial role in regulating cell death. There are different types of cell death, including apoptosis and necrosis, and autophagy can help prevent their occurrence by preventing the accumulation of damaged cellular components.
When autophagy is dysfunctional, these components can build up and trigger cell death, leading to various diseases. Autophagy can help prevent this by removing and recycling these components, promoting cell survival. Therefore, it’s important to maintain a healthy level of autophagy to prevent the accumulation of harmful cellular components and maintain cellular health.
Autophagy and Lysosomes
Autophagy and lysosomes are two processes that work hand-in-hand to maintain the health of our cells. Lysosomes are small organelles that act as the recycling centers of our cells. They contain a variety of enzymes that break down cellular waste and debris, converting them into usable components for the cell.
During the process of autophagy, lysosomes play a critical role in breaking down the contents of the autophagosome. As the autophagosome fuses with the lysosome, the lysosomal enzymes get to work breaking down the cellular components within the autophagosome, releasing their useful parts back into the cytoplasm.
This close relationship between autophagy and lysosomes highlights how our cells work together in complex ways to maintain our overall health. Without lysosomes, autophagy wouldn’t be able to effectively break down and recycle cellular components, and without autophagy, lysosomes would become overwhelmed with waste and debris.
Understanding the relationship between autophagy and lysosomes can give us insight into how we can support these processes in our own bodies to promote overall health and prevent disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, autophagy is a critical process that plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and preventing various diseases. By promoting autophagy, we may be able to slow down the aging process, reduce the risk of age-related diseases, and improve overall health. While there is still much to learn about autophagy, researchers are making exciting discoveries about its regulation and the compounds that can either promote or inhibit its function. As we continue to learn more about autophagy, we may be able to develop new treatments and therapies for a wide range of diseases.
Remember, promoting autophagy isn’t just about taking supplements or drugs. Simple lifestyle changes like fasting and exercise can also stimulate autophagy and provide various health benefits. So, why not give it a try and see how promoting autophagy can improve your overall health and well-being?
References
“Autophagy: Definition, Process & Regulation” – National Institute of Health – Reference
“The Role of Autophagy in Cancer” – Journal of Clinical Investigation – Reference
“Autophagy and Aging” – Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology – Reference
“Autophagy and Inflammation” – Annual Review of Immunology – Reference
“Autophagy and Mitochondria” – Journal of Molecular Biology – Reference
“Autophagy and the Immune System” – Annual Review of Immunology – Reference
“Autophagy and Apoptosis” – Cell Death and Differentiation – Reference
“Autophagy and Metabolism” – Nature Metabolism – Reference
“Autophagy and Protein Degradation” – Annual Review of Biochemistry – Reference
“Autophagy and Cell Death” – Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology – Reference