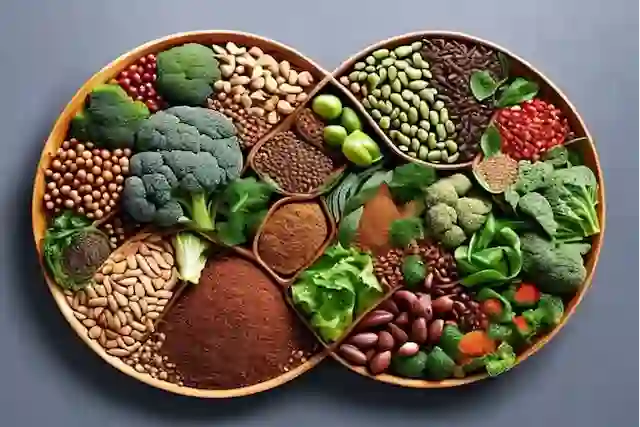
Introduction to Plant-Based High-Protein Diets
Welcome to the world of plant based high protein diets! In this article, we’ll explore the benefits, challenges, and practical tips for adopting this healthy, sustainable, and ethical lifestyle.
Why Choose a Plant-Based High-Protein Diet?
There are many reasons people might choose to adopt a plant-based high-protein diet, including health benefits, environmental impact, and ethical considerations.
Health Benefits
A plant-based high-protein diet can offer numerous health benefits, such as improved heart health, weight management, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases[^1^]. By prioritizing high-quality plant proteins, we can support our bodies with the nutrients they need to thrive. Additionally, plant-based diets have been shown to lower the risk of type 2 diabetes and certain types of cancer[^2^].
Environmental Impact
Adopting a plant-based high-protein diet can also help reduce our carbon footprint[^3^]. Plant-based diets use fewer natural resources, such as land and water, and produce less greenhouse gas emissions compared to animal-based diets.
Ethical Considerations
For those concerned about animal welfare, a plant-based high-protein diet is an excellent choice. By choosing plant-based proteins, we can support a more humane, sustainable food system.
Essential Amino Acids and Protein Sources
Amino Acids: The Building Blocks of Protein
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein, and there are nine essential amino acids that our bodies cannot produce on their own. It is important to ensure we consume these essential amino acids through our diet. Most plant-based protein sources contain all nine essential amino acids, though some may have lower levels of certain amino acids.
Top Plant-Based Protein Sources
There are plenty of high-quality plant-based protein sources to choose from:
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas, peas)
- Whole grains (quinoa, brown rice, barley, bulgur)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds, hemp seeds)
- Tofu, tempeh, and edamame
- Seitan (wheat gluten)
- Protein-rich vegetables (broccoli, spinach, kale)
Planning Your Plant-Based High-Protein Diet
Meal Planning Strategies
Balancing Macronutrients
When planning meals, aim to include a balance of macronutrients: protein, carbohydrates, and fats. This ensures you’ll receive all the necessary nutrients for optimal health.
Ensuring Nutrient Sufficiency
It’s important to consume a wide variety of plant-based foods to ensure you’re getting enough vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients. In particular, pay attention to nutrients that may be more challenging to obtain on a plant-based diet, such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids[^4^].
Protein-Packed Breakfast Ideas
Starting Your Day Strong
Begin your day with a protein-rich breakfast to help you stay energized and focused. Here are some plant-based high-protein breakfast ideas:
- Overnight oats with almond milk, chia seeds, and fresh fruit
- Smoothie with plant-based protein powder, spinach, and berries
- Tofu scramble with vegetables and whole-grain toast
Hearty Lunch and Dinner Options
Fueling Your Body Throughout the Day
Enjoy satisfying, protein-packed meals at lunch and dinner. Try these plant-based high-protein recipes:
- Chickpea and vegetable curry with brown rice
- Stuffed bell peppers with quinoa, black beans, and avocado
- Spaghetti with lentil Bolognese sauce
- Grilled portobello mushrooms with quinoa and roasted vegetables
- Buddha bowl with mixed greens, roasted chickpeas, sweet potato, and tahini dressing
Satisfying Snacks and Desserts
Here are some delicious plant-based high-protein snack and dessert ideas:
- Roasted chickpeas with your favorite spices
- Homemade energy balls made with dates, nuts, and seeds
- Chia seed pudding with fresh fruit
- Nut and seed butter on whole-grain crackers or apple slices
Tips for Success on a Plant-Based High-Protein Diet
Meeting Your Protein Needs
Keep track of your protein intake and adjust your meals accordingly to ensure you’re meeting your protein needs. You can use a food diary or an app to monitor your daily protein consumption.
Staying Full and Energized
A well-balanced plant-based high-protein diet can help you stay full and energized throughout the day. Make sure to include fiber-rich foods and healthy fats, such as avocado and nuts, to keep you satisfied.
Trying New Recipes and Ingredients
Experiment with new plant-based high-protein recipes and ingredients to keep your meals exciting and enjoyable. This will also help ensure you’re getting a diverse range of nutrients.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
There are some misconceptions about plant-based diets, such as the idea that they are low in protein or that you cannot build muscle on a plant-based diet. However, research has shown that with proper planning, a plant-based high-protein diet can provide all the necessary nutrients for optimal health and athletic performance[^5^].
Athletes and Plant-Based High-Protein Diets
Performance Benefits
Plant-based diets can offer performance benefits for athletes, such as improved recovery, reduced inflammation, and enhanced endurance[^6^]. A well-planned plant-based high-protein diet can support the needs of athletes at all levels.
Examples of Successful Plant-Based Athletes
Many successful athletes follow a plant-based diet, including:
- Venus Williams, professional tennis player
- Scott Jurek, ultramarathon runner
- David Carter, former NFL player
- Fiona Oakes, marathon runner and world record holder
These athletes have demonstrated that it is possible to excel in sports while following a plant-based high-protein diet.
Eating Out and Socializing on a Plant-Based High-Protein Diet
Finding Suitable Restaurants
Eating out can be an enjoyable part of a plant-based high-protein diet. Many restaurants now offer plant-based protein options, such as veggie burgers, tofu stir-fries, and grain bowls. Look for restaurants that offer a diverse menu and are open to accommodating your dietary preferences.
Sharing Your Dietary Preferences with Friends and Family
Communicate your dietary preferences with friends and family to ensure they are aware of your plant-based high-protein choices. Offer to bring a plant-based high-protein dish to share at gatherings, and suggest restaurants that cater to your dietary needs when dining out together.
Meal Prep Tips for a Plant-Based High-Protein Diet
Batch Cooking and Freezing
Batch cooking and freezing meals can save you time and make it easier to maintain a plant-based high-protein diet. Cook large portions of protein-rich staples, such as beans, lentils, and quinoa, and freeze them in individual servings for easy meal prep.
Utilizing Meal Planning Tools
There are many meal planning tools available, such as apps, websites, and cookbooks, that can help you plan and organize your plant-based high-protein meals. These resources can provide inspiration and guidance on creating balanced, nutrient-dense meals.
Combating Common Myths About Plant-Based High-Protein Diets
Myth: Plant-based diets are inherently low in protein
Fact: A well-planned plant-based diet can provide sufficient protein to meet your daily needs. Many plant-based foods, such as legumes, whole grains, and nuts, are rich in protein.
Myth: You need to consume animal products to get all essential amino acids
Fact: Most plant-based protein sources contain all nine essential amino acids, though some may have lower levels of certain amino acids. Consuming a diverse range of plant-based protein sources throughout the day ensures you’re getting all the essential amino acids you need.
Myth: Plant-based diets are not suitable for athletes
Fact: A well-planned plant-based high-protein diet can support the needs of athletes at all levels, providing adequate energy, nutrients, and protein for optimal performance and recovery.
Global Influences and Plant-Based High-Protein Cuisine
Exploring International Flavors
Plant-based high-protein diets can be inspired by various global cuisines, which often feature plant-based protein sources and flavor profiles. Some examples include:
- Indian cuisine: lentil curries, chickpea dishes, and vegetable stir-fries
- Middle Eastern cuisine: falafel, hummus, and tabbouleh
- Asian cuisine: tofu stir-fries, tempeh dishes, and edamame
- Mediterranean cuisine: bean salads, stuffed grape leaves, and whole-grain pasta dishes
Nutritional Supplements and Plant-Based High-Protein Diets
Considering Supplements
While a well-planned plant-based high-protein diet can provide most of the nutrients you need, some individuals may need to supplement with certain nutrients depending on their dietary choices and individual needs. Common supplements for those following a plant-based diet include:
- Vitamin B12: essential for nerve function and the production of red blood cells, this nutrient is primarily found in animal products, so supplementation is necessary for those on a plant-based diet.
- Iron: important for oxygen transport and energy production, plant-based iron sources may be less bioavailable than animal-based sources, so some individuals may need to supplement their diet with iron.
- Calcium: crucial for bone health, those who avoid dairy products may need to supplement with calcium to ensure adequate intake.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: essential for brain and heart health, plant-based sources of omega-3s may not be as efficiently converted by the body as animal-based sources, so supplementation with algae-derived omega-3s may be beneficial for some individuals.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before starting any supplementation, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to determine your individual needs and ensure you’re getting the appropriate nutrients in the right amounts.
Conclusion
A plant-based high-protein diet offers numerous health, environmental, and ethical benefits. By incorporating a variety of plant-based protein sources and planning well-balanced meals, you can meet your nutritional needs and support your overall well-being. Whether you’re an athlete or simply looking to improve your health, a plant-based high-protein diet is a sustainable and rewarding choice.
FAQs
-
- Is a plant-based high-protein diet suitable for everyone?
A well-planned plant-based high-protein diet can be suitable for people of all ages, activity levels, and health conditions, as long as they pay attention to nutrient sufficiency and balance their macronutrients. - Can I build muscle on a plant-based high-protein diet?
Yes, with proper meal planning and adequate protein intake, you can effectively build muscle on a plant-based high-protein diet. - Do I need to take supplements on a plant-based high-protein diet?
Some individuals may need to supplement with nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids, depending on their dietary choices and individual needs. - What are some high-protein plant-based alternatives to meat?
Tofu, tempeh, seitan, legumes, and whole grains are all excellent high-protein plant-based alternatives to meat. - Do I need to combine different plant-based protein sources to get all essential amino acids?
While some plant-based protein sources may have lower levels of certain essential amino acids, it’s not necessary to combine them in every meal. Consuming a varied diet throughout the day will ensure you’re getting all the essential amino acids you need.
- Is a plant-based high-protein diet suitable for everyone?
References
- Plant-based diets for cardiovascular disease prevention: All plant foods are not created equal – Reference
- Protein content of various plant-based foods – Reference
- USDA National Nutrient Database – Reference
- Plant-based diets and athletic performance – Reference
- Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Vegetarian Diets – Reference
- Plant-based protein sources: A guide to the best options – Reference
- Position of the American Dietetic Association and Dietitians of Canada: Vegetarian diets – Reference
- The environmental impact of plant-based diets: How does it compare to animal-based diets? – Reference
- The effects of a plant-based diet on athletic performance – Reference
- Plant-based diets: A review of the literature – Reference